Tutorial: Read related data - ASP.NET MVC with EF Core
In the previous tutorial, you completed the School data model. In this tutorial, you'll read and display related data -- that is, data that the Entity Framework loads into navigation properties.
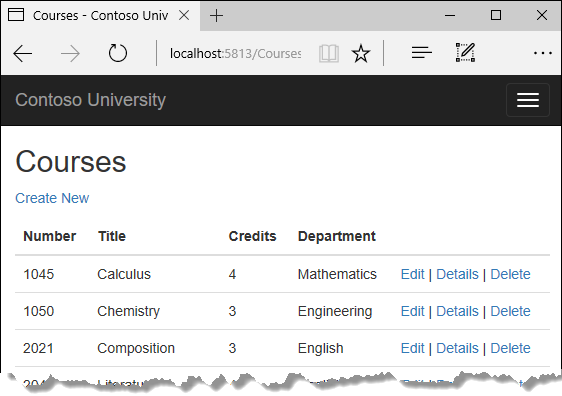
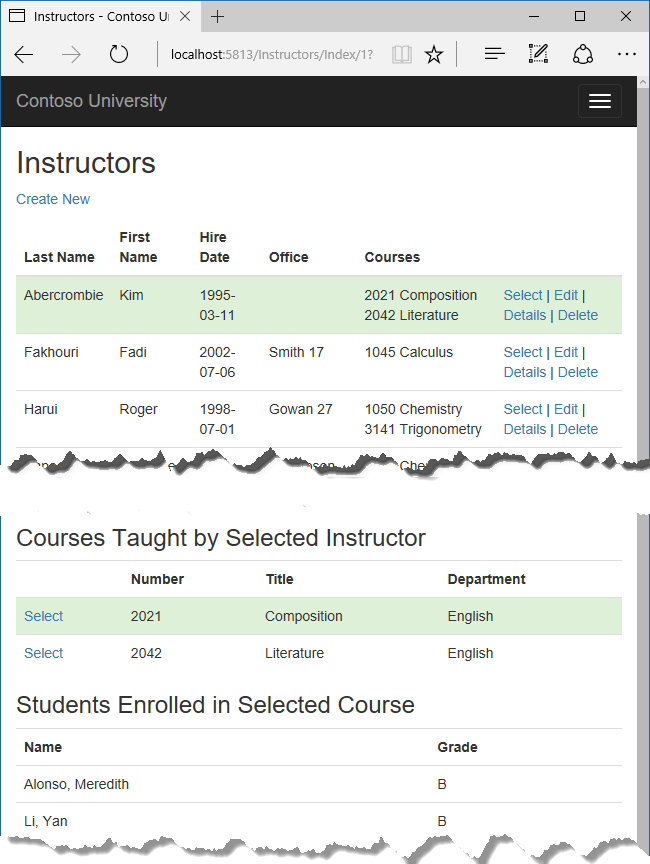
The following illustrations show the pages that you'll work with.
In this tutorial, you:
- Learn how to load related data
- Create a Courses page
- Create an Instructors page
- Learn about explicit loading
Prerequisites
Learn how to load related data
There are several ways that Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) software such as Entity Framework can load related data into the navigation properties of an entity:
Eager loading: When the entity is read, related data is retrieved along with it. This typically results in a single join query that retrieves all of the data that's needed. You specify eager loading in Entity Framework Core by using the
IncludeandThenIncludemethods.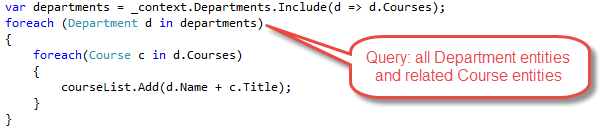
You can retrieve some of the data in separate queries, and EF "fixes up" the navigation properties. That is, EF automatically adds the separately retrieved entities where they belong in navigation properties of previously retrieved entities. For the query that retrieves related data, you can use the
Loadmethod instead of a method that returns a list or object, such asToListorSingle.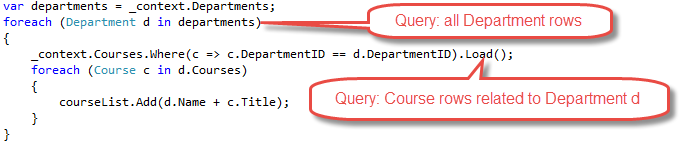
Explicit loading: When the entity is first read, related data isn't retrieved. You write code that retrieves the related data if it's needed. As in the case of eager loading with separate queries, explicit loading results in multiple queries sent to the database. The difference is that with explicit loading, the code specifies the navigation properties to be loaded. In Entity Framework Core 1.1 you can use the
Loadmethod to do explicit loading. For example: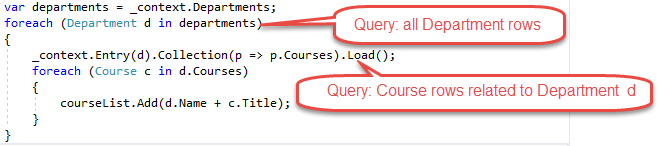
Lazy loading: When the entity is first read, related data isn't retrieved. However, the first time you attempt to access a navigation property, the data required for that navigation property is automatically retrieved. A query is sent to the database each time you try to get data from a navigation property for the first time. Entity Framework Core 1.0 doesn't support lazy loading.
Performance considerations
If you know you need related data for every entity retrieved, eager loading often offers the best performance, because a single query sent to the database is typically more efficient than separate queries for each entity retrieved. For example, suppose that each department has ten related courses. Eager loading of all related data would result in just a single (join) query and a single round trip to the database. A separate query for courses for each department would result in eleven round trips to the database. The extra round trips to the database are especially detrimental to performance when latency is high.
On the other hand, in some scenarios separate queries is more efficient. Eager loading of all related data in one query might cause a very complex join to be generated, which SQL Server can't process efficiently. Or if you need to access an entity's navigation properties only for a subset of a set of the entities you're processing, separate queries might perform better because eager loading of everything up front would retrieve more data than you need. If performance is critical, it's best to test performance both ways in order to make the best choice.
Create a Courses page
The Course entity includes a navigation property that contains the Department entity of the department that the course is assigned to. To display the name of the assigned department in a list of courses, you need to get the Name property from the Department entity that's in the Course.Department navigation property.
Create a controller named CoursesController for the Course entity type, using the same options for the MVC Controller with views, using Entity Framework scaffolder that you did earlier for the StudentsController, as shown in the following illustration:
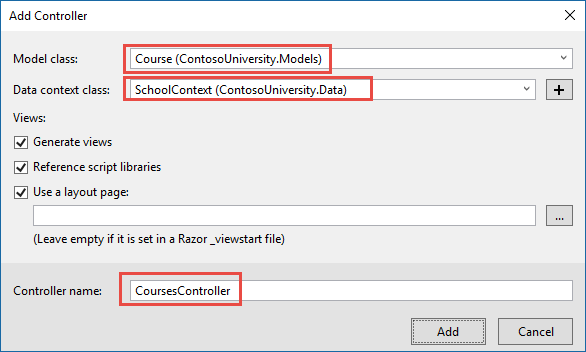
Open CoursesController.cs and examine the Index method. The automatic scaffolding has specified eager loading for the Department navigation property by using the Include method.
Replace the Index method with the following code that uses a more appropriate name for the IQueryable that returns Course entities (courses instead of schoolContext):
public async Task<IActionResult> Index()
{
var courses = _context.Courses
.Include(c => c.Department)
.AsNoTracking();
return View(await courses.ToListAsync());
}
Open Views/Courses/Index.cshtml and replace the template code with the following code. The changes are highlighted:
@model IEnumerable<ContosoUniversity.Models.Course>
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Courses";
}
<h2>Courses</h2>
<p>
<a asp-action="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.CourseID)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Title)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Credits)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Department)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.CourseID)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Credits)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Department.Name)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@item.CourseID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-action="Details" asp-route-id="@item.CourseID">Details</a> |
<a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@item.CourseID">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
You've made the following changes to the scaffolded code:
Changed the heading from Index to Courses.
Added a Number column that shows the
CourseIDproperty value. By default, primary keys aren't scaffolded because normally they're meaningless to end users. However, in this case the primary key is meaningful and you want to show it.Changed the Department column to display the department name. The code displays the
Nameproperty of theDepartmententity that's loaded into theDepartmentnavigation property:@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Department.Name)
Run the app and select the Courses tab to see the list with department names.

Create an Instructors page
In this section, you'll create a controller and view for the Instructor entity in order to display the Instructors page:

This page reads and displays related data in the following ways:
The list of instructors displays related data from the
OfficeAssignmententity. TheInstructorandOfficeAssignmententities are in a one-to-zero-or-one relationship. You'll use eager loading for theOfficeAssignmententities. As explained earlier, eager loading is typically more efficient when you need the related data for all retrieved rows of the primary table. In this case, you want to display office assignments for all displayed instructors.When the user selects an instructor, related
Courseentities are displayed. TheInstructorandCourseentities are in a many-to-many relationship. You'll use eager loading for theCourseentities and their relatedDepartmententities. In this case, separate queries might be more efficient because you need courses only for the selected instructor. However, this example shows how to use eager loading for navigation properties within entities that are themselves in navigation properties.When the user selects a course, related data from the
Enrollmentsentity set is displayed. TheCourseandEnrollmententities are in a one-to-many relationship. You'll use separate queries forEnrollmententities and their relatedStudententities.
Create a view model for the Instructor Index view
The Instructors page shows data from three different tables. Therefore, you'll create a view model that includes three properties, each holding the data for one of the tables.
In the SchoolViewModels folder, create InstructorIndexData.cs and replace the existing code with the following code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContosoUniversity.Models.SchoolViewModels
{
public class InstructorIndexData
{
public IEnumerable<Instructor> Instructors { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<Course> Courses { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; }
}
}
Create the Instructor controller and views
Create an Instructors controller with EF read/write actions as shown in the following illustration:
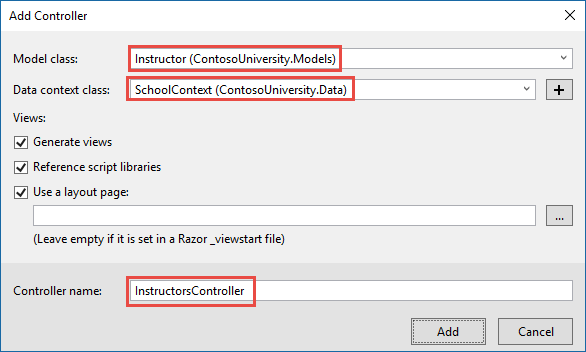
Open InstructorsController.cs and add a using statement for the ViewModels namespace:
using ContosoUniversity.Models.SchoolViewModels;
Replace the Index method with the following code to do eager loading of related data and put it in the view model.
public async Task<IActionResult> Index(int? id, int? courseID)
{
var viewModel = new InstructorIndexData();
viewModel.Instructors = await _context.Instructors
.Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Enrollments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Student)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Department)
.AsNoTracking()
.OrderBy(i => i.LastName)
.ToListAsync();
if (id != null)
{
ViewData["InstructorID"] = id.Value;
Instructor instructor = viewModel.Instructors.Where(
i => i.ID == id.Value).Single();
viewModel.Courses = instructor.CourseAssignments.Select(s => s.Course);
}
if (courseID != null)
{
ViewData["CourseID"] = courseID.Value;
viewModel.Enrollments = viewModel.Courses.Where(
x => x.CourseID == courseID).Single().Enrollments;
}
return View(viewModel);
}
The method accepts optional route data (id) and a query string parameter (courseID) that provide the ID values of the selected instructor and selected course. The parameters are provided by the Select hyperlinks on the page.
The code begins by creating an instance of the view model and putting in it the list of instructors. The code specifies eager loading for the Instructor.OfficeAssignment and the Instructor.CourseAssignments navigation properties. Within the CourseAssignments property, the Course property is loaded, and within that, the Enrollments and Department properties are loaded, and within each Enrollment entity the Student property is loaded.
viewModel.Instructors = await _context.Instructors
.Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Enrollments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Student)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Department)
.AsNoTracking()
.OrderBy(i => i.LastName)
.ToListAsync();
Since the view always requires the OfficeAssignment entity, it's more efficient to fetch that in the same query. Course entities are required when an instructor is selected in the web page, so a single query is better than multiple queries only if the page is displayed more often with a course selected than without.
The code repeats CourseAssignments and Course because you need two properties from Course. The first string of ThenInclude calls gets CourseAssignment.Course, Course.Enrollments, and Enrollment.Student.
You can read more about including multiple levels of related data here.
viewModel.Instructors = await _context.Instructors
.Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Enrollments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Student)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Department)
.AsNoTracking()
.OrderBy(i => i.LastName)
.ToListAsync();
At that point in the code, another ThenInclude would be for navigation properties of Student, which you don't need. But calling Include starts over with Instructor properties, so you have to go through the chain again, this time specifying Course.Department instead of Course.Enrollments.
viewModel.Instructors = await _context.Instructors
.Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Enrollments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Student)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Department)
.AsNoTracking()
.OrderBy(i => i.LastName)
.ToListAsync();
The following code executes when an instructor was selected. The selected instructor is retrieved from the list of instructors in the view model. The view model's Courses property is then loaded with the Course entities from that instructor's CourseAssignments navigation property.
if (id != null)
{
ViewData["InstructorID"] = id.Value;
Instructor instructor = viewModel.Instructors.Where(
i => i.ID == id.Value).Single();
viewModel.Courses = instructor.CourseAssignments.Select(s => s.Course);
}
The Where method returns a collection, but in this case the criteria passed to that method result in only a single Instructor entity being returned. The Single method converts the collection into a single Instructor entity, which gives you access to that entity's CourseAssignments property. The CourseAssignments property contains CourseAssignment entities, from which you want only the related Course entities.
You use the Single method on a collection when you know the collection will have only one item. The Single method throws an exception if the collection passed to it's empty or if there's more than one item. An alternative is SingleOrDefault, which returns a default value (null in this case) if the collection is empty. However, in this case that would still result in an exception (from trying to find a Courses property on a null reference), and the exception message would less clearly indicate the cause of the problem. When you call the Single method, you can also pass in the Where condition instead of calling the Where method separately:
.Single(i => i.ID == id.Value)
Instead of:
.Where(i => i.ID == id.Value).Single()
Next, if a course was selected, the selected course is retrieved from the list of courses in the view model. Then the view model's Enrollments property is loaded with the Enrollment entities from that course's Enrollments navigation property.
if (courseID != null)
{
ViewData["CourseID"] = courseID.Value;
viewModel.Enrollments = viewModel.Courses.Where(
x => x.CourseID == courseID).Single().Enrollments;
}
Tracking vs no-tracking
No-tracking queries are useful when the results are used in a read-only scenario. They're generally quicker to execute because there's no need to set up the change tracking information. If the entities retrieved from the database don't need to be updated, then a no-tracking query is likely to perform better than a tracking query.
In some cases a tracking query is more efficient than a no-tracking query. For more information, see Tracking vs. No-Tracking Queries.
Modify the Instructor Index view
In Views/Instructors/Index.cshtml, replace the template code with the following code. The changes are highlighted.
@model ContosoUniversity.Models.SchoolViewModels.InstructorIndexData
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Instructors";
}
<h2>Instructors</h2>
<p>
<a asp-action="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Hire Date</th>
<th>Office</th>
<th>Courses</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Instructors)
{
string selectedRow = "";
if (item.ID == (int?)ViewData["InstructorID"])
{
selectedRow = "table-success";
}
<tr class="@selectedRow">
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstMidName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.HireDate)
</td>
<td>
@if (item.OfficeAssignment != null)
{
@item.OfficeAssignment.Location
}
</td>
<td>
@foreach (var course in item.CourseAssignments)
{
@course.Course.CourseID @course.Course.Title <br />
}
</td>
<td>
<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Select</a> |
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-action="Details" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> |
<a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
@model ContosoUniversity.Models.SchoolViewModels.InstructorIndexData
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Instructors";
}
<h2>Instructors</h2>
<p>
<a asp-action="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Hire Date</th>
<th>Office</th>
<th>Courses</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Instructors)
{
string selectedRow = "";
if (item.ID == (int?)ViewData["InstructorID"])
{
selectedRow = "success";
}
<tr class="@selectedRow">
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstMidName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.HireDate)
</td>
<td>
@if (item.OfficeAssignment != null)
{
@item.OfficeAssignment.Location
}
</td>
<td>
@foreach (var course in item.CourseAssignments)
{
@course.Course.CourseID @course.Course.Title <br />
}
</td>
<td>
<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Select</a> |
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-action="Details" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> |
<a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
You've made the following changes to the existing code:
Changed the model class to
InstructorIndexData.Changed the page title from Index to Instructors.
Added an Office column that displays
item.OfficeAssignment.Locationonly ifitem.OfficeAssignmentisn't null. (Because this is a one-to-zero-or-one relationship, there might not be a related OfficeAssignment entity.)@if (item.OfficeAssignment != null) { @item.OfficeAssignment.Location }Added a Courses column that displays courses taught by each instructor. For more information, see the Explicit line transition section of the Razor syntax article.
Added code that conditionally adds a Bootstrap CSS class to the
trelement of the selected instructor. This class sets a background color for the selected row.Added a new hyperlink labeled Select immediately before the other links in each row, which causes the selected instructor's ID to be sent to the
Indexmethod.<a asp-action="Index" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Select</a> |
Run the app and select the Instructors tab. The page displays the Location property of related OfficeAssignment entities and an empty table cell when there's no related OfficeAssignment entity.
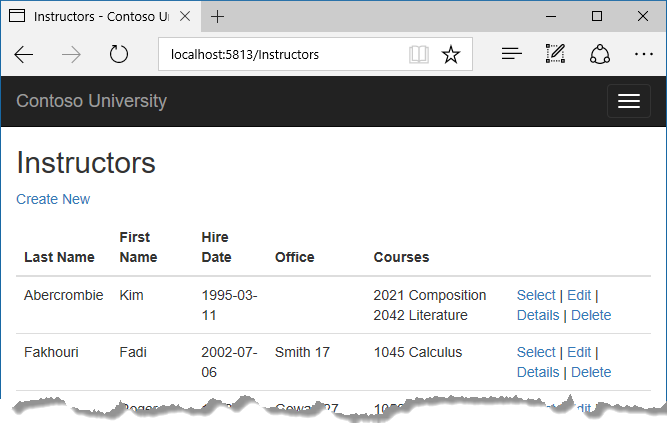
In the Views/Instructors/Index.cshtml file, after the closing table element (at the end of the file), add the following code. This code displays a list of courses related to an instructor when an instructor is selected.
@if (Model.Courses != null)
{
<h3>Courses Taught by Selected Instructor</h3>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>Number</th>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Department</th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model.Courses)
{
string selectedRow = "";
if (item.CourseID == (int?)ViewData["CourseID"])
{
selectedRow = "success";
}
<tr class="@selectedRow">
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Select", "Index", new { courseID = item.CourseID })
</td>
<td>
@item.CourseID
</td>
<td>
@item.Title
</td>
<td>
@item.Department.Name
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
}
This code reads the Courses property of the view model to display a list of courses. It also provides a Select hyperlink that sends the ID of the selected course to the Index action method.
Refresh the page and select an instructor. Now you see a grid that displays courses assigned to the selected instructor, and for each course you see the name of the assigned department.
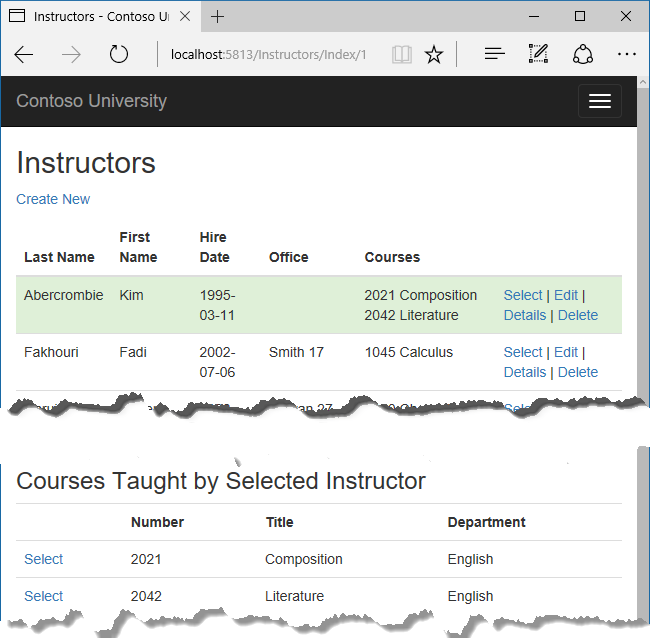
After the code block you just added, add the following code. This displays a list of the students who are enrolled in a course when that course is selected.
@if (Model.Enrollments != null)
{
<h3>
Students Enrolled in Selected Course
</h3>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Grade</th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model.Enrollments)
{
<tr>
<td>
@item.Student.FullName
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Grade)
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
}
This code reads the Enrollments property of the view model in order to display a list of students enrolled in the course.
Refresh the page again and select an instructor. Then select a course to see the list of enrolled students and their grades.

About explicit loading
When you retrieved the list of instructors in InstructorsController.cs, you specified eager loading for the CourseAssignments navigation property.
Suppose you expected users to only rarely want to see enrollments in a selected instructor and course. In that case, you might want to load the enrollment data only if it's requested. To see an example of how to do explicit loading, replace the Index method with the following code, which removes eager loading for Enrollments and loads that property explicitly. The code changes are highlighted.
public async Task<IActionResult> Index(int? id, int? courseID)
{
var viewModel = new InstructorIndexData();
viewModel.Instructors = await _context.Instructors
.Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment)
.Include(i => i.CourseAssignments)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Course)
.ThenInclude(i => i.Department)
.OrderBy(i => i.LastName)
.ToListAsync();
if (id != null)
{
ViewData["InstructorID"] = id.Value;
Instructor instructor = viewModel.Instructors.Where(
i => i.ID == id.Value).Single();
viewModel.Courses = instructor.CourseAssignments.Select(s => s.Course);
}
if (courseID != null)
{
ViewData["CourseID"] = courseID.Value;
var selectedCourse = viewModel.Courses.Where(x => x.CourseID == courseID).Single();
await _context.Entry(selectedCourse).Collection(x => x.Enrollments).LoadAsync();
foreach (Enrollment enrollment in selectedCourse.Enrollments)
{
await _context.Entry(enrollment).Reference(x => x.Student).LoadAsync();
}
viewModel.Enrollments = selectedCourse.Enrollments;
}
return View(viewModel);
}
The new code drops the ThenInclude method calls for enrollment data from the code that retrieves instructor entities. It also drops AsNoTracking. If an instructor and course are selected, the highlighted code retrieves Enrollment entities for the selected course, and Student entities for each Enrollment.
Run the app, go to the Instructors Index page now and you'll see no difference in what's displayed on the page, although you've changed how the data is retrieved.
Get the code
Download or view the completed application.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you:
- Learned how to load related data
- Created a Courses page
- Created an Instructors page
- Learned about explicit loading
Advance to the next tutorial to learn how to update related data.
ASP.NET Core
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
